
AI in Psychiatry Practices: What Works and What’s Just Hype
Discover key insights on practical, proven uses of AI in psychiatry practices—and how Psychiatry-Cloud’s All In Intelligence helps clinicians focus on care.
A Psychiatry EHR That Drives Revenue—With Billing Services That Maximize It.
Our psychiatry-specific EHR enhances patient, clinical, and billing journeys from the start—with expert billers improving collections, reducing denials, and keeping you informed every step of the way.

At Psychiatry-Cloud, we’re All In Intelligence—because our AI is the answer to true freedom and low-friction practice management. AI agents weave directly into the everyday tasks that slow practices down—charting, coding, scheduling, billing. You’ll see real relief, not another feature to manage.
From intake to charting to claims, our agents handle the busywork so you don’t have to.
Every tool connects in one platform, eliminating extra logins, duplicate entry, and hidden add-ons.
Designed by a practicing physician, our EHR for psychiatry practices solves the daily challenges providers face—not theoretical ones.
The result: fewer admin headaches, more focus on what matters, and true freedom to run your practice the way you want.
“It’s just easy to use. All of the providers just think it’s very simple to learn, easy to use, you can navigate quickly. And then having the billing taken off of our hands is very important.”
— Jennifer Erdman, NP
“When I opened this clinic in August of 2023, I started my practice with approximately 360 patients. As of now… I have more than doubled my amount of patients in the span of a year.”
— Jessica Koupal, DNP-FNP, PMHNP, QMHP
“I would highly recommend their RCM services, as it helped me streamline my practice workflow giving me higher profit margins and frees up more time for myself and my family.”
— Ramneesh Baweja, MD
“The Virtual Front Desk Assistants are an integral part of my practice even though they are not physically here. Hands down, they have saved my practice.”
— Mitchell Cabisudo, MD
Our psychiatry-specific EHR combines tailored workflows with AI agents that anticipate what you need, reduce wasted time, and simplify the business side of practice management.

Sessions end, but the work doesn’t. Another detailed note waits, and the next patient is already at the door. Evenings slip away to catch-up charting. Sound familiar?
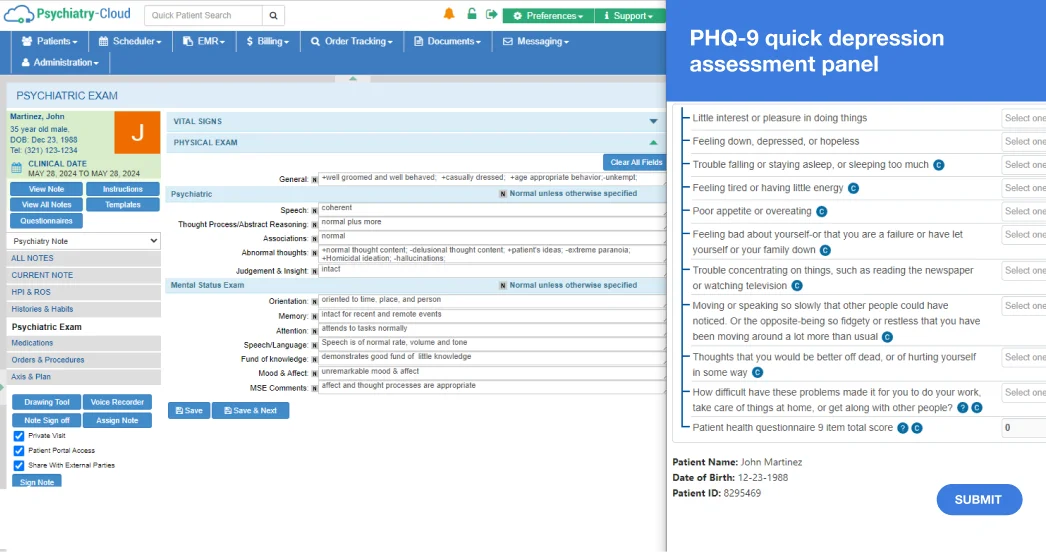
Need a specialty-specific note? Our EHR comes preloaded with a full library of chart structures tailored to psychiatrists and mental health professionals. And if you don’t find what you’re looking for? Create custom plug-and-play templates that you can save and use whenever you need them.
Revenue Optimization
Vitality Psychiatry Group Practice faced mounting challenges with its billing processes. With Psychiatry-Cloud’s EHR and practice management services, it reached new TMS revenue heights—while reducing admin work for staff.
Patient Growth
Ocean Psychological Services faced significant challenges in handling recruitment, onboarding, and HR processes as a growing practice. Our Virtual Assistants took on these tasks, leaving room for accelerated patient growth.
Compliance Perfection
Carolina Behavioral Healthcare faced challenges with MIPS compliance, including difficulty understanding requirements and maintaining accurate documentation. Our Compliance Services team took this practice’s MIPS score from 39% to 100% in no time.
You’ve done everything right, but the claim still comes back denied. Payments lag, staff chase down payors, and patients grow frustrated.
In case you need extra billing support, we have you covered. Our mental health billing services boast the best results in the industry*:
*Results from individual clients. Actual metrics may vary.

Discover key insights on practical, proven uses of AI in psychiatry practices—and how Psychiatry-Cloud’s All In Intelligence helps clinicians focus on care.

Discover how a mental health virtual assistant helps psychiatry practices cut costs, streamline admin work, and grow without sacrificing care quality.

A strong psychiatry reputation builds trust, attracts new patients, and strengthens your brand. Learn proven ways to manage your behavioral health reputation.